- IQ Test
- All Tests
- IQ Practice Test
- IQ Challenges
- Result Sample
Diagrammatic reasoning practice enhances your ability to understand, interpret, and analyze Diagrammatic reasoning practice sharpens your ability to interpret, analyze, and solve visual information and abstract patterns. These tests are essential for developing skills such as logical thinking, pattern recognition, and problem-solving. They also enhance spatial reasoning, decision-making, and cognitive flexibility, which are valuable for technical and analytical roles.
With an extensive collection of questions (thousands of diagrammatic reasoning questions), users can explore a wide variety of visual problems. Detailed explanations accompany the answers, ensuring you gain a clear understanding of each solution and improve your performance effectively.
Each test consists of 9 questions, with difficulty levels progressively increasing to match the participant's abilities.
You must complete all the questions. Upon finishing the test, your results will be provided instantly, free of charge.
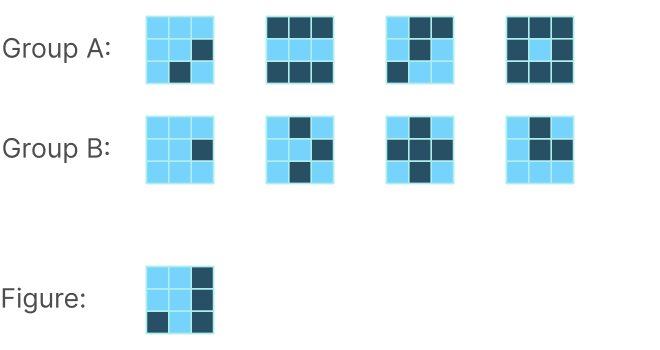

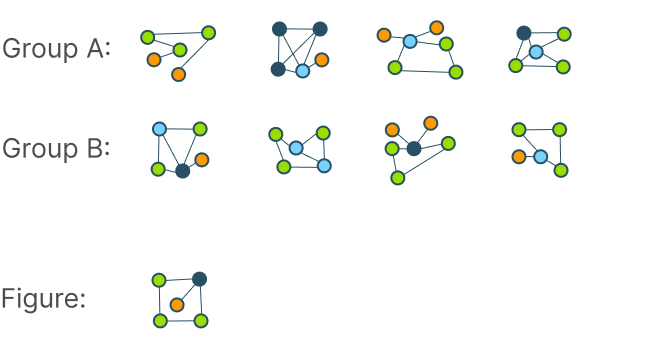
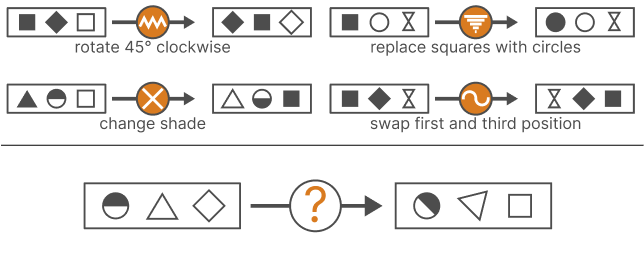
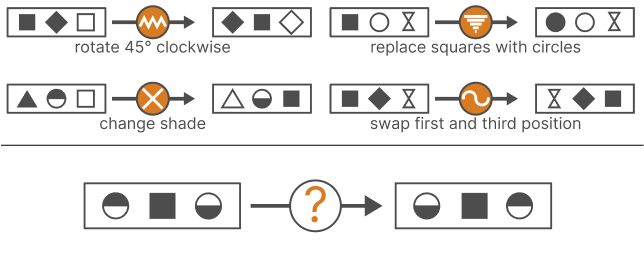
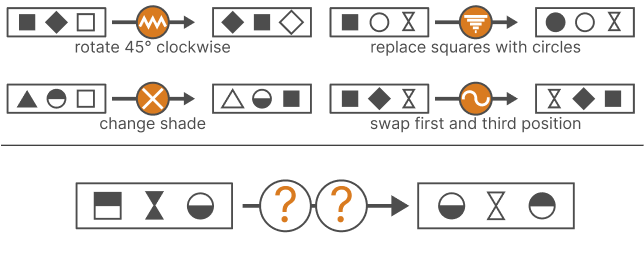
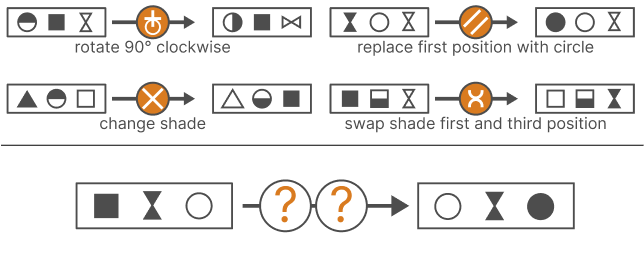
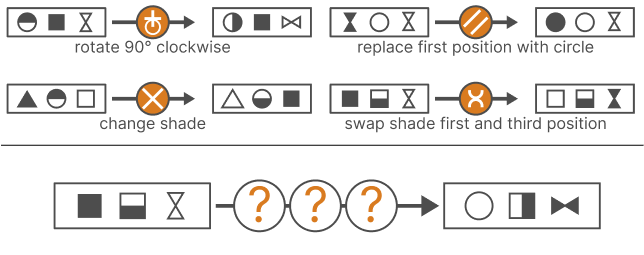
Diagrammatic reasoning is a critical cognitive skill, enabling individuals to interpret patterns, analyze abstract structures, and deduce rules from visual information. This ability is particularly essential for excelling in IQ tests and pre-employment assessments that demand logic, pattern recognition, and diagram-based problem-solving. In this article, we delve into the significance of diagrammatic reasoning, the key elements of these tests, and tips for effective practice.
A Diagrammatic Reasoning Practice evaluates an individual’s capacity to work through information presented in diagrams or pictorial formats.
These tests are commonly used in:
In these tests, candidates infer rules, recognize patterns, and identify logical relationships. The primary focus is on analyzing the structure and flow of diagrams rather than testing domain-specific knowledge.
Diagrammatic reasoning tests are designed to measure several cognitive abilities, including:
Diagrammatic reasoning is often part of broader logical reasoning tests. Below are common test types:
1. Inductive Reasoning
2. Diagrammatic Reasoning
3. Deductive Reasoning
Effective preparation is key to mastering diagrammatic reasoning tests.
Below are strategies to enhance your performance:
Common Uses of Diagrammatic Reasoning Tests
Diagrammatic reasoning tests are widely used across different fields as useful instruments of evaluation and training.
Most notably, such tests are always used in the course of recruitment within the initial stages in order to screen candidates. Employers use them to gauge a candidate’s analytical aptitude and anything involving logic is usually paired to a problem solving type job that requires a lot of brain work, such as engineering, IT, finance & management consulting jobs. Through fair understanding of who has the logical ability and space judgment employers can reduce time and effort and choose the most appropriate candidate for the job.
Moreover, diagrammatic reasoning tests represent an essential part of education assessments and evaluations. They are used frequently with I.Q tests and aptitude exams, and can offer useful information about a person’s ability and potential in academic or technical subject areas, especially the professions involving higher levels of mathematics, logic, research and technology, including the sciences and engineering.
Besides using it in the process of recruitment and vocational training, this type of tests can be viewed as useful ways to develop essential skills. Participation in these tests may even help to increase an individual’s logical mind, problem solving skills and spatial awareness. Through drills that involve the solving of different forms of diagrammatic reasoning, the participants are able to attain flexibility of thinking processes, searching, ability to analyze information, and improved patterns of acknowledgement, which are highly desirable in any endeavor in life and in the working world.
Success in diagrammatic reasoning tests hinges on a multi-faceted approach.
Firstly, deepening pattern recognition is crucial. This involves meticulously analyzing diagrams to identify core rules governing shape changes, positional shifts, and additions/deletions. Practicing with diverse diagram types, including simple and complex sequences, as well as rule-based problems, broadens pattern recognition capabilities.
Second, for any learning disability to be counteracted there must be a boost in visual spatial skills. This can be done by the following tasks: mental rotation (included in puzzles, games, visuals), and spatial reasoning (consisting of drawings and buildings).
Third, it implies building efficient test-taking approaches as a critical component of the learning process. This includes timetabling, applying the elimination method and keeping to a cool head during the exam period.
Fourthly, leveraging practice resources is crucial. This involves utilizing online platforms, books, and seeking feedback on practice tests to identify areas for improvement.
Last but not the least, the conditions conducive for studying must be established, as well. This includes reducing interference, concentrating on working and avoiding getting exhausted. When these strategies are performed with consistency and oftentimes when individuals perform them with actual dedication, there will be massive improvement found in how one approaches diagrammatic reasoning tests as well as in general performance on tests that contain such reasoning.
Diagrammatic reasoning tests are one of the best tools in order to assess the applicable knowledge of the candidates, as well as their general abilities to think logically and solve problems. Everybody needs practice and concentration irrespective of whether It is an IQ test, a pre- employment test or only wanting an improved brain. Take advantage of every tip and resource outlined in this guide and go farther in your diagrammatic reasoning skills and abilities.